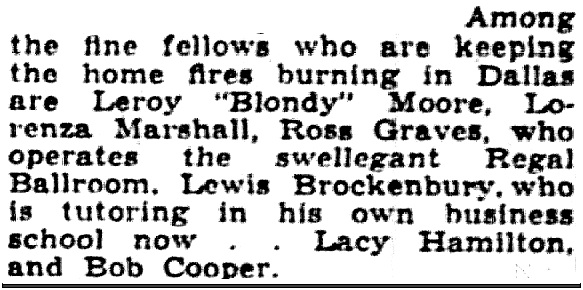Deep Ellum: Life Along Central Track
 The heart of Deep Ellum… (Dallas Public Library photo)
The heart of Deep Ellum… (Dallas Public Library photo)
by Paula Bosse
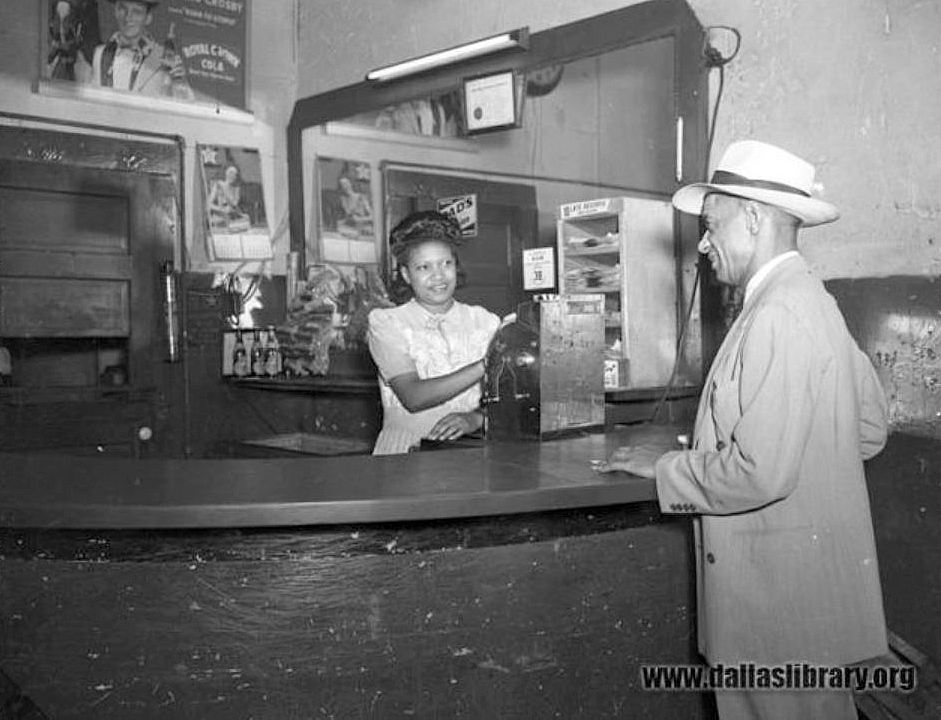
One of my happiest Flashback Dallas research deep-dives resulted in the post “The Gypsy Tea Room, Central Avenue, and The Darensbourg Brothers.” It was prompted by a photo I had seen for years but had never really known what it showed. I loved writing that, and I’m so happy that it is a perennially popular post. Here is that original photo, below, which shows people walking along the row of barber shops, cafes, pool rooms, domino parlors, taverns, and other businesses:
The view is to the south — Elm Street is in the distance, where that building juts out to the left. The street about the same distance away to the north (behind the photographer) was Pacific. Someone walking out of the Gypsy Tea Room would have been facing the old train depot. Between the depot and the block of businesses were railroad tracks (not in frequent use in the 1930s, the time of these photos) — the unpaved road that ran alongside the tracks was Central Avenue (when North Central Expressway was built years later, it closely followed the path of these railroad tracks). This general area was considered the heart of Deep Ellum and was filled with Black-owned retail establishments and was a gathering place for social activities and entertainment.
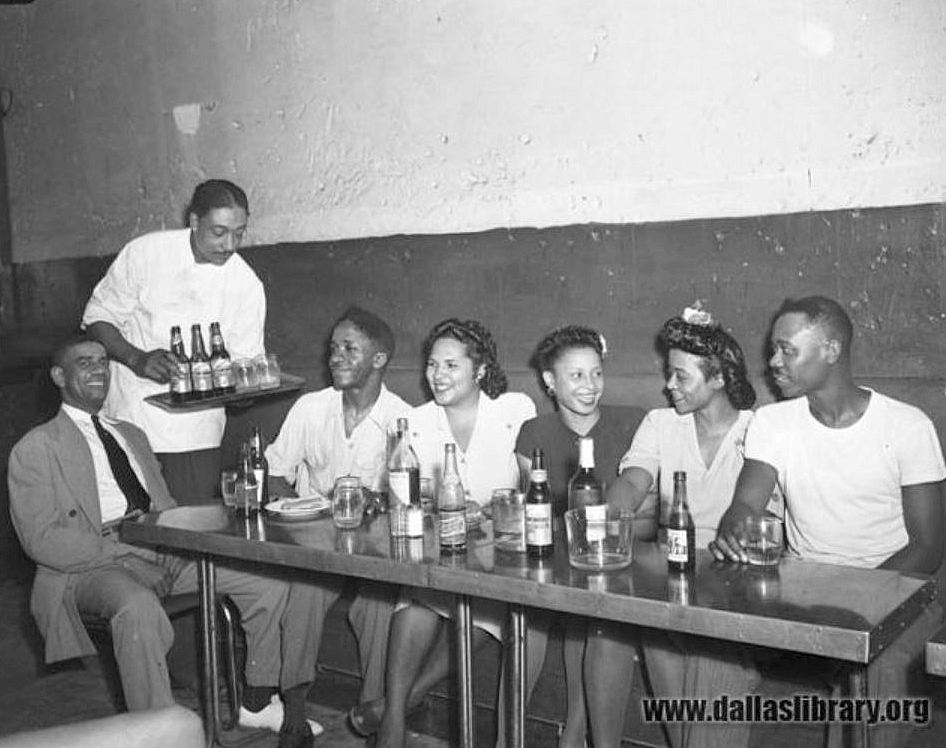
A while back, I came across two other photos, which I recognized as being “companion” photos to the “Gypsy Tea Room” one — the one at the very top of this post, and the one below.
The photo immediately above shows the Roosevelt Cafe, which was at 201 N. Central, and the North Pole Domino Parlor (a partial window sign is seen at the right), at 207 Central. A train is passing. This photo and the photo at the very top both show partial signs for Black Dallas beer. (All images are larger when clicked.)
For a better idea of where these photos were taken, see the map below (it shows a detail from a 1921 map — about 15 years before these photos were taken). (See the larger, full Sanborn map here.)
 1921 Sanborn map (det) showing where photos were taken
1921 Sanborn map (det) showing where photos were taken
*
These are just great, great photos. There aren’t enough photographs like this which capture everyday life in Dallas’ minority communities. Deep Ellum was a thriving Black area at the time. Read a contemporary description of the good things and the bad things going on in this vibrant neighborhood in a (mostly uncondescending) chapter in the WPA Guide to Dallas, “Deep Ellum: Harlem in Miniature.”
**
What about “Black Dallas Beer”? I haven’t found a lot about it, but it apparently began as a Dallas-brewed beer in the 1930s but was later brewed elsewhere. (A mention of its Schepps Beer affiliation is here.)
 1937, via Taverntrove.com
1937, via Taverntrove.com
 U.S. Patent Office bulletin, Sept. 8, 1936
U.S. Patent Office bulletin, Sept. 8, 1936
“Don’t be a sissy! Drink Black Dallas Beer — Made Without Sugar.”
 Waco Times-Herald, May 22, 1937
Waco Times-Herald, May 22, 1937
A “Famous Black Dallas Malt Liquor” popped up a few decades later — at that point, there was no connection to Dallas, except for the name and the fantastic label boasting the Dallas skyline. “Smooth as Evening Dusk.”
***
Sources & Notes
The top Dallas Public Library photo — “[African American men walking and sitting along North Central Avenue in downtown Dallas in the early 1930’s]” — is from the Saxon Collection, Texas/Dallas History & Archives Division of the Dallas Public Library; its call number is PA85-16/4.
The second photo — “Gypsy Tea Room Cafe located in Deep Ellum” — is from the WPA Dallas Guide & History Collection of the Dallas Public Library — its call number is PA85-16/22.
The third photo — “[African American men seated on benches and standing outside of the Roosevelt Cafe in downtown Dallas in the 1930’s]” — is from the Saxon Collection, Texas/Dallas History & Archives Division of the Dallas Public Library; its call number is PA85-16/5.
Much more info on this Deep Ellum block can be found in the previously linked post from 2015, “The Gypsy Tea Room, Central Avenue, and The Darensbourg Brothers.”
See my other Flashback Dallas posts on Deep Ellum here.

*
Copyright © 2024 Paula Bosse. All Rights Reserved.































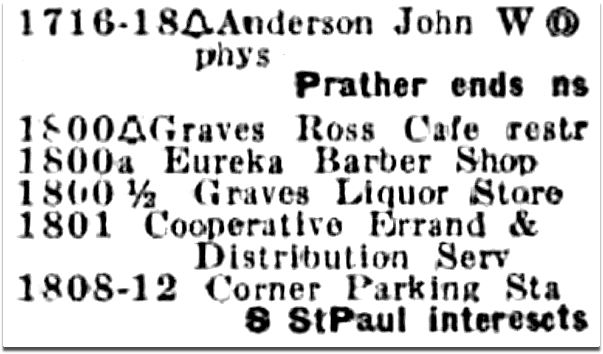
 1967 Dallas directory
1967 Dallas directory

















 Bright’s Drug Store, 6327 Hillcrest, University Park
Bright’s Drug Store, 6327 Hillcrest, University Park